Disposal costs have become a growing concern for households, facilities managers, and businesses across the UK. What was once a straightforward service has evolved into a highly regulated, infrastructure-heavy industry with rising operational demands.

Understanding why disposal costs continue to increase is essential for anyone responsible for managing waste budgets. These price rises are not arbitrary. They reflect deeper changes in environmental regulation, labour markets, fuel pricing, and the long-term shift away from landfill dependency.
This guide explains what is really driving disposal costs, how these pressures affect different sectors, and what practical steps organisations can take to manage expenses without compromising compliance or sustainability.
Key Takeaways
- Disposal costs are rising due to regulation, taxation, labour, and fuel pressures
- Landfill taxes play a major role in increasing per-tonne charges
- Commercial waste handling is more complex than residential collection
- Poor segregation directly increases disposal expenses
- Strategic planning can significantly reduce long-term costs
Why Disposal Costs Are Increasing Nationwide
Disposal costs are no longer tied only to collection and transport. Modern waste handling involves sorting, treatment, reporting, and compliance with strict environmental standards.
The UK’s commitment to reducing landfill use has reshaped the entire sector. As a result, businesses now pay for a full chain of services rather than a single collection event. This structural shift explains why prices continue to rise even when volumes stay the same.
The Evolution of the Waste Management Industry

From Simple Collection to Regulated Infrastructure
Historically, waste disposal involved limited sorting and minimal oversight. Today, every stage is documented, monitored, and regulated.
Service providers must comply with environmental legislation, maintain certified vehicles, and deliver materials to licensed facilities. Each requirement adds operational cost, which is reflected in disposal charges.
Environmental Compliance as a Cost Driver
Stricter rules are designed to protect public health and reduce environmental damage. However, compliance requires:
- Advanced sorting facilities
- Trained staff
- Auditing and reporting systems
- Approved treatment routes
These safeguards improve sustainability but increase overall disposal costs.
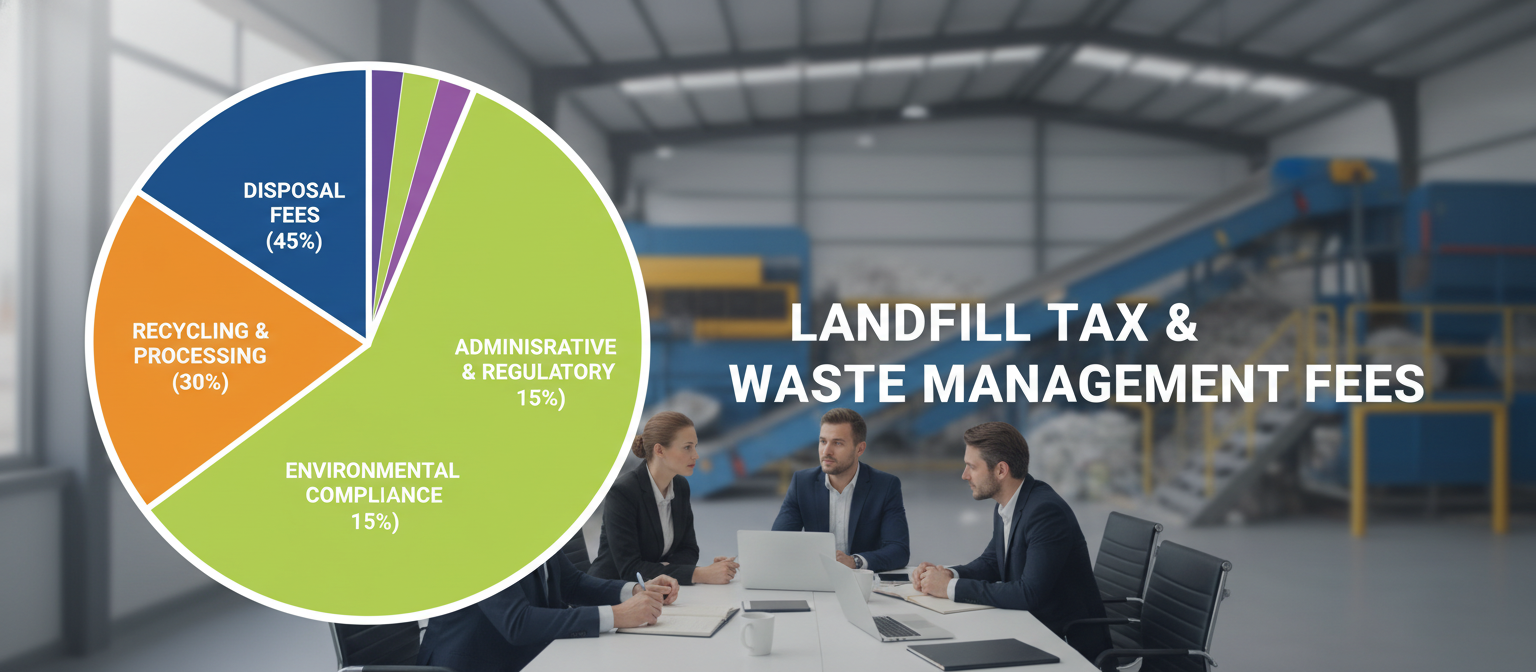
Breaking Down Disposal Costs
Understanding disposal costs starts with knowing what you are paying for. Charges are typically a combination of processing fees, government taxes, and operational expenses.
Landfill Tax and Processing Fees
The UK landfill tax was introduced to discourage landfill use and promote recycling. It increases annually and applies to most non-recyclable materials.
Processing facilities charge by weight and material type, with mixed waste being the most expensive due to manual sorting requirements.
Example Disposal Costs by Material Type (UK)
| Material Type | Typical Cost per Tonne |
|---|---|
| Mixed general waste | High |
| Construction waste | High |
| Green waste | Medium |
| Inert materials | Low |
| Hazardous materials | Very high |
(Indicative ranges only – costs vary by region and facility)
Labour, Fuel, and Maintenance Costs
Disposal costs also reflect rising operational expenses:
- Skilled drivers and trained handling staff
- Fuel for heavy vehicles
- Vehicle maintenance and safety inspections
- Insurance and compliance administration
Fuel volatility alone has a significant impact, particularly for services covering large geographic areas.
How Disposal Costs Affect Businesses
Small Businesses vs Larger Organisations
Smaller companies often feel rising disposal costs more sharply due to limited bargaining power and tighter margins. Larger organisations may secure volume-based pricing but face complex multi-site waste streams.
Regardless of size, poor waste planning leads to unnecessary spending.
Businesses dealing with higher volumes often benefit from understanding planning large-scale junk removal projects , as poor planning frequently leads to unnecessary charges.
Indirect Financial Impact
Disposal costs are not limited to invoices. Missed collections, overflowing bins, or non-compliance can result in:
- Workplace hygiene issues
- Customer complaints
- Regulatory penalties
- Operational disruption
These indirect costs often exceed the service charge itself.
Disposal Costs UK: Cashflow and Budget Planning
Managing disposal costs effectively requires predictable pricing and transparent contracts.
Businesses benefit from:
- Clear pricing structures
- Flexible payment schedules
- Regular service reviews
- No automatic contract escalations
Treating disposal as a controllable operational expense rather than a fixed cost opens opportunities for optimisation.
Practical Strategies to Reduce Disposal Costs
Waste Audits and Source Reduction
A waste audit identifies what is being discarded and why. Many businesses discover that a large proportion of their waste could be recycled at lower cost.
Reducing waste at the source is the most effective long-term strategy.
Correct Bin Selection and Collection Frequency
Oversized containers and unnecessary collections inflate disposal costs. Adjusting bin size and collection schedules to actual usage prevents paying for unused capacity.
Recycling and Segregation: The Biggest Cost Lever
Proper segregation significantly reduces disposal costs. Recyclable materials often incur lower processing fees than mixed waste.
Common cost-saving streams include:
- Cardboard and paper
- Plastics
- Glass
- Food waste
Contamination of recycling bins, however, can result in higher charges, making staff training essential.
Alternatives to Landfill Disposal
When recycling is not possible, waste-to-energy facilities offer a more sustainable alternative. These facilities generate energy while avoiding landfill tax, often resulting in lower overall disposal costs.
Regulatory Responsibilities and Legal Compliance
All businesses have a legal duty to ensure their waste is handled correctly.
This includes:
- Using licensed waste carriers
- Retaining Waste Transfer Notes
- Ensuring waste reaches authorised facilities
Failure to comply can lead to fines and reputational damage, adding further hidden costs.
For official guidance, see: UK Government – Landfill Tax Overview
Industry Trends Shaping Future Disposal Costs
Several trends suggest disposal costs will continue to rise:
- Ongoing landfill tax increases
- Higher environmental standards
- Labour shortages
- Increased reporting requirements
At the same time, digital service tools and data-driven waste management are helping businesses regain control and identify efficiencies.
Conclusion
Disposal costs are rising for structural reasons, not short-term fluctuations. Environmental policy, infrastructure investment, and operational realities all contribute to higher prices.
However, businesses are not powerless. By understanding cost drivers, improving segregation, reviewing container usage, and planning proactively, disposal costs can be managed effectively.
The cheapest option is rarely the best value. Reliability, compliance, and transparency protect organisations from hidden expenses and operational risk.
With informed decisions and a strategic approach, it is possible to control disposal costs while meeting sustainability and legal obligations.